Discover the intriguing truth about avian predation as we delve into the question, “Do crows eat other birds?” Uncover fascinating insights into crow behavior and its impact on avian ecosystems.
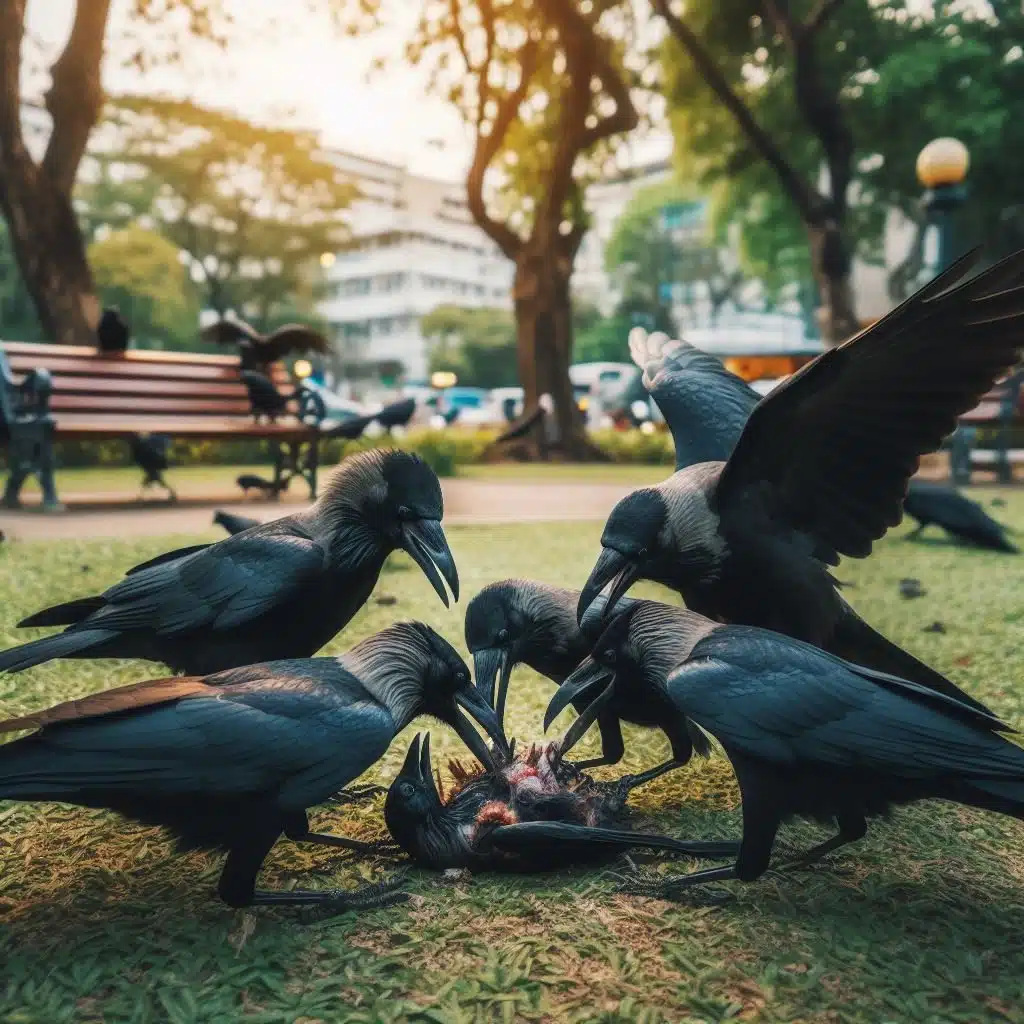
Crows, renowned for their intelligence and adaptability, have long intrigued bird enthusiasts and scientists alike. Among the myriad of behaviors exhibited by these corvids, one question frequently arises: Do crows engage in predation on other birds? In this comprehensive article, we explore the complex relationship between crows and their avian counterparts, shedding light on their dietary habits, ecological roles, and the factors influencing their predatory behavior.
The Nature of Crow Predation
Crows, opportunistic omnivores, possess a diverse diet ranging from fruits and seeds to small mammals and insects. Despite their predominantly omnivorous nature, instances of avian predation by crows have been observed, sparking curiosity regarding their predatory behavior towards other birds.
Exploring Avian Predation: Fact or Fiction?
Amidst numerous anecdotal accounts of crows preying on other birds, scientific research provides valuable insights into the reality of this behavior. While crows primarily feed on carrion and small vertebrates, documented cases of predation on nestlings and eggs of other bird species have been reported.
Unveiling the Evidence: Observations and Studies
Field observations and scientific studies have contributed significantly to our understanding of crow predation patterns. Research conducted in diverse habitats has revealed instances of crows raiding nests of songbirds and waterfowl, indicating a nuanced relationship between crows and their avian prey.
Factors Influencing Crow Predatory Behavior
The predation behavior of crows is influenced by a myriad of factors, including ecological dynamics, resource availability, and social interactions within crow communities.
Ecological Dynamics: Competition and Resource Exploitation
In ecosystems where resources are scarce, competition among bird species intensifies, potentially leading crows to resort to avian predation as a supplemental food source. Additionally, habitat alterations and human disturbances can influence the foraging behavior of crows, impacting their interactions with other bird species.
Social Interactions: Learning and Innovation
Crows exhibit remarkable social learning abilities, enabling them to acquire and transmit knowledge about foraging techniques, including avian predation, within their social groups. Through observational learning and innovation, crows may refine their predatory strategies, further influencing their interactions with other bird species.
Understanding the Implications
The predation of other birds by crows carries significant ecological implications, influencing avian community dynamics and ecosystem stability.
Ecological Consequences: Balancing Act in Avian Ecosystems
While avian predation by crows can regulate populations of certain bird species, it may also exert pressure on vulnerable populations, especially those already facing habitat loss or fragmentation. Understanding the nuanced effects of crow predation is crucial for maintaining ecological balance within avian ecosystems.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Are crows considered apex predators?
Crows are not typically classified as apex predators due to their varied diet and interactions with other predators within their ecosystems. While they may exhibit predatory behavior towards smaller birds, they coexist with larger avian and mammalian predators.
Do crows eat the eggs of other birds?
Yes, crows have been documented consuming the eggs of various bird species, particularly when opportunities arise during the breeding season. Their omnivorous diet and opportunistic foraging behavior make them capable egg predators.
How do crows locate bird nests?
Crows possess keen observational skills and may employ various strategies to locate bird nests, including visual cues, vocalizations, and social learning. Additionally, crows may opportunistically follow other bird species to discover potential nesting sites.
Do crows pose a threat to endangered bird species?
In certain cases, crows may pose a threat to endangered bird species, particularly if populations are already vulnerable due to habitat loss or other anthropogenic factors. However, the extent of their impact varies depending on ecological conditions and conservation efforts.
Can bird feeders attract crows?
Bird feeders may attract a variety of bird species, including crows, depending on the types of seeds and feed offered. While crows are known to exploit supplementary food sources, their presence at bird feeders is influenced by local habitat characteristics and competition with other birds.
How can I deter crows from raiding bird nests?
Implementing strategies such as installing deterrent devices, modifying nesting habitats, and minimizing attractants can help reduce the risk of crow predation on bird nests. However, it’s essential to consider the broader ecological context and potential impacts on other wildlife species.
30 Amazing Facts About Crows – Interesting Facts about Crows
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether crows eat other birds unveils a fascinating aspect of avian ecology and behavior. While crows primarily exhibit omnivorous feeding habits, instances of avian predation underscore the complexity of their interactions within avian ecosystems. By delving into the intricacies of crow predation, we gain valuable insights into the dynamics shaping avian communities and the delicate balance of nature.






